
Meta has launched a recent artificial intelligence (AI) model that understands video much like how humans understand the world. It's much like learning just by watching, without having to be told what's happening. The reason is that it improves the machine's understanding of the world by analyzing the interactions between objects and scenes within the video.
On the sixteenth (local time), Meta released 'V-JEPA', an AI model that predicts and generates missing or obscured parts in videos, through its blog.
This model was developed by senior AI scientist Yann LeCun Mehta and is an AI architecture developed to grasp video in the same method to humans. Unlike existing generative AI models that try to reconstruct missing parts of a video on the pixel level, it’s a nongenerative AI model that predicts missing or obscured areas in an abstract representation space.
Which means that the model doesn’t generate recent content or fill in missing pixels directly. As an alternative, it predicts missing parts of the video by dividing each frame of the video into large blocks and learning the semantic space information between blocks and the detailed information between frames that occur over time.
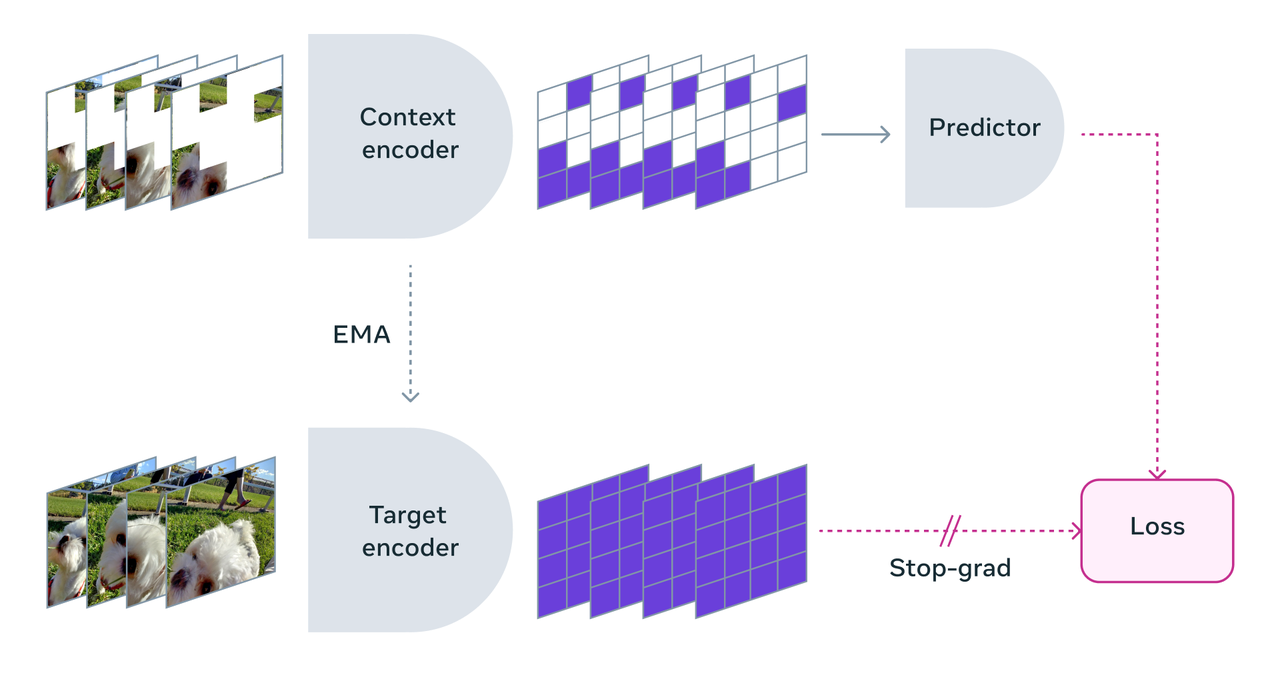
“V-Zepha works best at distinguishing between fine-grained object interactions and detailed object-to-object interactions that occur over time,” Mehta said. For instance, the model can determine whether someone puts down their pen, or whether someone puts the pen down. It is feasible to inform the difference between picking up a pen and pretending to place it down, but currently only in a brief time period, about 10 seconds.
Moreover, V-Zepha is characterised by learning from unlabeled videos. It's like children learn just by watching and don't need someone to inform them what's happening. This makes learning faster and more efficient. Slightly than attempting to fill every pixel, it focuses on finding missing parts within the video in a wise way.
Mehta claimed that V-Zepha can improve training efficiency by 1.5 to six times since it eliminates the necessity to collect and analyze every pixel for each frame of video.
In the longer term, Meta plans to expand the functionality of V-Zepha by integrating audio in order that it may possibly process audio content together with video. Is currently githubIt may well be used for research purposes.
Reporter Park Chan cpark@aitimes.com