
The worldwide marketplace for humanoid robots is anticipated to achieve $38 billion (about 51.2 trillion won) in 2035. This figure is greater than six times higher than the $6 billion (roughly 8 trillion won) expected only a 12 months ago. That is evidence that humanoid development has accelerated with the introduction of artificial intelligence (AI).
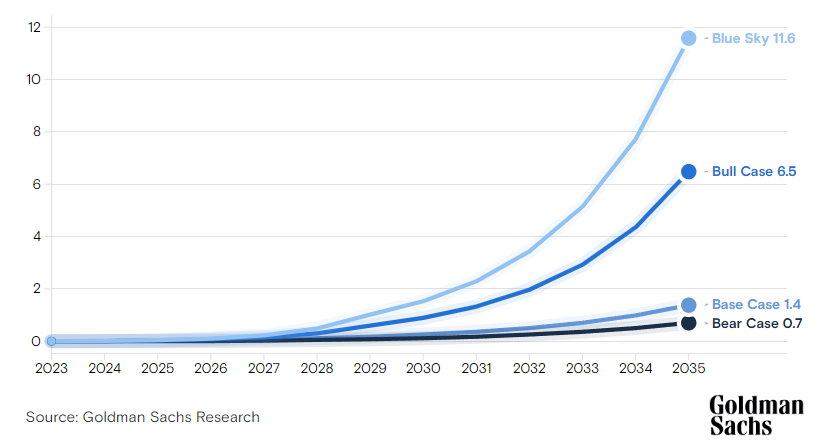
Goldman Sachs announced in a recent report that the worldwide market size for humanoid robots will reach $38 billion in 2035, and robot shipments will reach 1.4 million units.
It is a six-fold increase in market size and a four-fold increase in shipment volume in comparison with the report released by Goldman Sachs last 12 months. As well as, robot manufacturing costs are predicted to be reduced by 40%, and profitability is anticipated to be achieved quickly.
The largest reason was the introduction of enormous language models (LLM), and he said, “AI development surprised us probably the most.” The adoption of LLMs in robotics began to realize prominence last 12 months. It will greatly help the robot make decisions and act by itself without the necessity for engineers to code the whole lot into the robot.
One other necessary point is that the value of robot parts, from high-precision gears to actuators, has change into cheaper than previously expected. The production cost of humanoids was predicted to be $50,000 to $250,000 (roughly 67 to 340 million won) per unit last 12 months, but this 12 months it was lowered to $30,000 to $150,000 (roughly 40 to 200 million won). Analysts expected production costs to fall by 15 to twenty percent per 12 months, but they really fell by as much as 40 percent.
It is because cheaper components have entered the market, supply chains have diversified, and design and manufacturing techniques have evolved. Because of this, it’s predicted that factory humanoids will likely be distributed one 12 months earlier and consumer humanoids will likely be distributed two to 4 years sooner than previously expected.
Goldman Sachs predicted that 250,000 units will likely be shipped for industrial use alone by 2030. Nevertheless, it is anticipated that consumer use will increase rapidly in 10 years and can exceed 1 million units produced annually by 2035.
It is anticipated that robot manufacturing capabilities will likely be dispersed by country. In other words, the evaluation is that some countries, equivalent to america, will change into the middle of sophisticated AI software, while Asia will change into a production hub with an in depth supply chain and low manufacturing costs.
As well as, the undeniable fact that many players are emerging on this field and capital is being concentrated was seen as a positive factor. Recently, global big tech, automobile corporations, and even countries equivalent to China are specializing in it.
There are also signs that the majority hardware for humanoid robots is already available, or at the very least approaching maturity. The evaluation is that the majority cameras, motors, force sensors, mobile transmissions, and batteries are able to be used for business purposes.
However, problems equivalent to difficulty in increasing production of some parts that require high-precision processing and long manufacturing cycles were seen as obstacles. Moreover, AI technology still has lots of room for advancement.
Use cases for humanoids will likely concentrate on 'dangerous, dirty and boring' tasks, just like current factory automation. That is because of the demand from corporations that want to resolve the issue of manpower alternative and reduce costs. Humanoids have the advantage of being more flexible than current factory automation and having the ability to expand into more precise fields.
Assuming a alternative rate of 5 to fifteen percent for hazardous labor equivalent to automobile manufacturing, disaster relief, and nuclear reactor work, global demand for humanoid robots could reach 1.1 to three.5 million units, it said. Particularly, parts manufacturing was chosen as the sphere with the very best demand.
“In a best-case scenario where innovation unfolds rapidly and demand surges, humanoid robots may be expected to change into the ‘next generation of essential devices,’ like smartphones or EVs,” Goldman Sachs said. “Robots will likely be essential for manufacturing and dangerous tasks. After all, it could actually even be helpful in elderly care, etc.”
Reporter Lim Da-jun ydj@aitimes.com