What when you could see what you’re imagining in a photograph? It looks like a distant future, but artificial intelligence (AI) is making it possible. Recently, Japan has developed a technology that converts human brain waves into images using AI technology.
Vice reported on the 4th that a research team at Osaka University in Japan has developed a technology that converts brain waves from functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) scans of the visually stimulated brain into photographic images using ‘Stable Diffusion’, an AI model for generating images. An fMRI scanner is a sort of non-invasive brain imaging technology that detects brain activity by measuring changes in blood flow.
The research team used fMRI to scan the activity of neurons within the brain area chargeable for vision when subjects viewed facial images. It was then fed right into a stable diffusion model to generate accurate images based on the fMRI scan information.
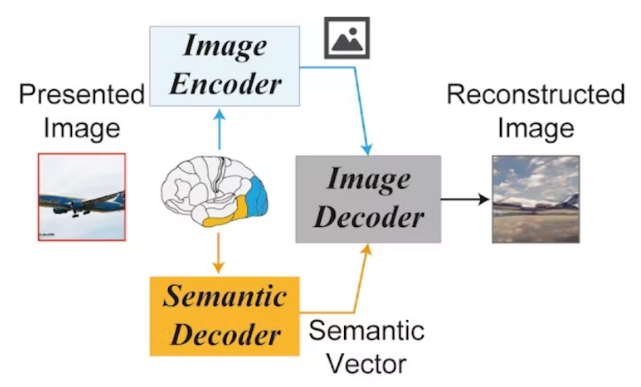
The fMRI machine captures brain signals while the topic views the photographs. A small linear model is used to predict the potential representation of a picture from fMRI data. A possible representation of a picture is a compressed version of the image containing only essentially the most relevant features.
The anticipated result becomes a picture roughly representing the fMRI data. This rough image is processed by the autoencoder’s encoder and noise is added through a diffusion process.
Then, the fMRI signals measured within the upper brain regions are used to decode potential textual representations. The rough image and text representation generated in this manner are supplied to the denoising model and passed to the decoding module of the autoencoder to generate the ultimate image.

This technology could be utilized in various fields. It could help police discover suspects or help them communicate with patients by reading and translating brain waves of comatose patients into images. Additionally it is helpful in restoring sight to those that have been blinded by illness or accidents.
Chan Park, cpark@aitimes.com
