That is an example on easy methods to deploy the open-source LLMs, like BLOOM to Amazon SageMaker for inference using the brand new Hugging Face LLM Inference Container.
We’ll deploy the 12B Pythia Open Assistant Model, an open-source Chat LLM trained with the Open Assistant dataset.
The instance covers:
- Setup development environment
- Retrieve the brand new Hugging Face LLM DLC
- Deploy Open Assistant 12B to Amazon SageMaker
- Run inference and chat with our model
- Create Gradio Chatbot backed by Amazon SageMaker
You could find the code for the instance also within the notebooks repository.
What’s Hugging Face LLM Inference DLC?
Hugging Face LLM DLC is a brand new purpose-built Inference Container to simply deploy LLMs in a secure and managed environment. The DLC is powered by Text Generation Inference (TGI), an open-source, purpose-built solution for deploying and serving Large Language Models (LLMs). TGI enables high-performance text generation using Tensor Parallelism and dynamic batching for the preferred open-source LLMs, including StarCoder, BLOOM, GPT-NeoX, Llama, and T5.
Text Generation Inference is already utilized by customers equivalent to IBM, Grammarly, and the Open-Assistant initiative implements optimization for all supported model architectures, including:
Officially supported model architectures are currently:
With the brand new Hugging Face LLM Inference DLCs on Amazon SageMaker, AWS customers can profit from the identical technologies that power highly concurrent, low latency LLM experiences like HuggingChat, OpenAssistant, and Inference API for LLM models on the Hugging Face Hub.
Let’s start!
1. Setup development environment
We’re going to use the sagemaker python SDK to deploy BLOOM to Amazon SageMaker. We want to be sure that to have an AWS account configured and the sagemaker python SDK installed.
!pip install "sagemaker==2.175.0" --upgrade --quiet
In the event you are going to make use of Sagemaker in an area environment, you wish access to an IAM Role with the required permissions for Sagemaker. You could find here more about it.
import sagemaker
import boto3
sess = sagemaker.Session()
sagemaker_session_bucket=None
if sagemaker_session_bucket is None and sess is not None:
sagemaker_session_bucket = sess.default_bucket()
try:
role = sagemaker.get_execution_role()
except ValueError:
iam = boto3.client('iam')
role = iam.get_role(RoleName='sagemaker_execution_role')['Role']['Arn']
sess = sagemaker.Session(default_bucket=sagemaker_session_bucket)
print(f"sagemaker role arn: {role}")
print(f"sagemaker session region: {sess.boto_region_name}")
2. Retrieve the brand new Hugging Face LLM DLC
In comparison with deploying regular Hugging Face models, we first have to retrieve the container uri and supply it to our HuggingFaceModel model class with a image_uri pointing to the image. To retrieve the brand new Hugging Face LLM DLC in Amazon SageMaker, we are able to use the get_huggingface_llm_image_uri method provided by the sagemaker SDK. This method allows us to retrieve the URI for the specified Hugging Face LLM DLC based on the desired backend, session, region, and version. You could find the available versions here
from sagemaker.huggingface import get_huggingface_llm_image_uri
llm_image = get_huggingface_llm_image_uri(
"huggingface",
version="1.0.3"
)
print(f"llm image uri: {llm_image}")
3. Deploy Open Assistant 12B to Amazon SageMaker
Note: Quotas for Amazon SageMaker can vary between accounts. In the event you receive an error indicating you’ve got exceeded your quota, you’ll be able to increase them through the Service Quotas console.
To deploy Open Assistant Model to Amazon SageMaker we create a HuggingFaceModel model class and define our endpoint configuration including the hf_model_id, instance_type etc. We’ll use a g5.12xlarge instance type, which has 4 NVIDIA A10G GPUs and 96GB of GPU memory.
Note: We could also optimize the deployment for cost and use g5.2xlarge instance type and enable int-8 quantization.
import json
from sagemaker.huggingface import HuggingFaceModel
instance_type = "ml.g5.12xlarge"
number_of_gpu = 4
health_check_timeout = 300
config = {
'HF_MODEL_ID': "OpenAssistant/pythia-12b-sft-v8-7k-steps",
'SM_NUM_GPUS': json.dumps(number_of_gpu),
'MAX_INPUT_LENGTH': json.dumps(1024),
'MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS': json.dumps(2048),
}
llm_model = HuggingFaceModel(
role=role,
image_uri=llm_image,
env=config
)
After we’ve got created the HuggingFaceModel we are able to deploy it to Amazon SageMaker using the deploy method. We’ll deploy the model with the ml.g5.12xlarge instance type. TGI will mechanically distribute and shard the model across all GPUs.
llm = llm_model.deploy(
initial_instance_count=1,
instance_type=instance_type,
container_startup_health_check_timeout=health_check_timeout,
)
SageMaker will now create our endpoint and deploy the model to it. This could take 5-10 minutes.
4. Run inference and chat with our model
After our endpoint is deployed we are able to run inference on it using the predict method from the predictor. We will use different parameters to regulate the generation, defining them within the parameters attribute of the payload. As of today TGI supports the next parameters:
temperature: Controls randomness within the model. Lower values will make the model more deterministic and better values will make the model more random. Default value is 1.0.max_new_tokens: The utmost variety of tokens to generate. Default value is 20, max value is 512.repetition_penalty: Controls the likelihood of repetition, defaults tonull.seed: The seed to make use of for random generation, default isnull.stop: A listing of tokens to stop the generation. The generation will stop when one in every of the tokens is generated.top_k: The variety of highest probability vocabulary tokens to maintain for top-k-filtering. Default value isnull, which disables top-k-filtering.top_p: The cumulative probability of parameter highest probability vocabulary tokens to maintain for nucleus sampling, default tonulldo_sample: Whether or not to make use of sampling; use greedy decoding otherwise. Default value isfalse.best_of: Generate best_of sequences and return the one if the best token logprobs, default tonull.details: Whether or to not return details in regards to the generation. Default value isfalse.return_full_text: Whether or to not return the complete text or only the generated part. Default value isfalse.truncate: Whether or to not truncate the input to the utmost length of the model. Default value istrue.typical_p: The everyday probability of a token. Default value isnull.watermark: The watermark to make use of for the generation. Default value isfalse.
You could find the open api specification of TGI within the swagger documentation
The OpenAssistant/pythia-12b-sft-v8-7k-steps is a conversational chat model meaning we are able to chat with it using the next prompt:
<|prompter|>[Instruction]<|endoftext|>
<|assistant|>
lets give it a primary try to ask about some cool ideas to do in the summertime:
chat = llm.predict(endoftext)
print(chat[0]["generated_text"])
Now we’ll show easy methods to use generation parameters within the parameters attribute of the payload. Along with setting custom temperature, top_p, etc, we also stop generation after the turn of the bot.
prompt="""<|prompter|>How am i able to stay more energetic during winter? Give me 3 suggestions.<|endoftext|><|assistant|>"""
payload = {
"inputs": prompt,
"parameters": endoftext
}
response = llm.predict(payload)
print(response[0]["generated_text"])
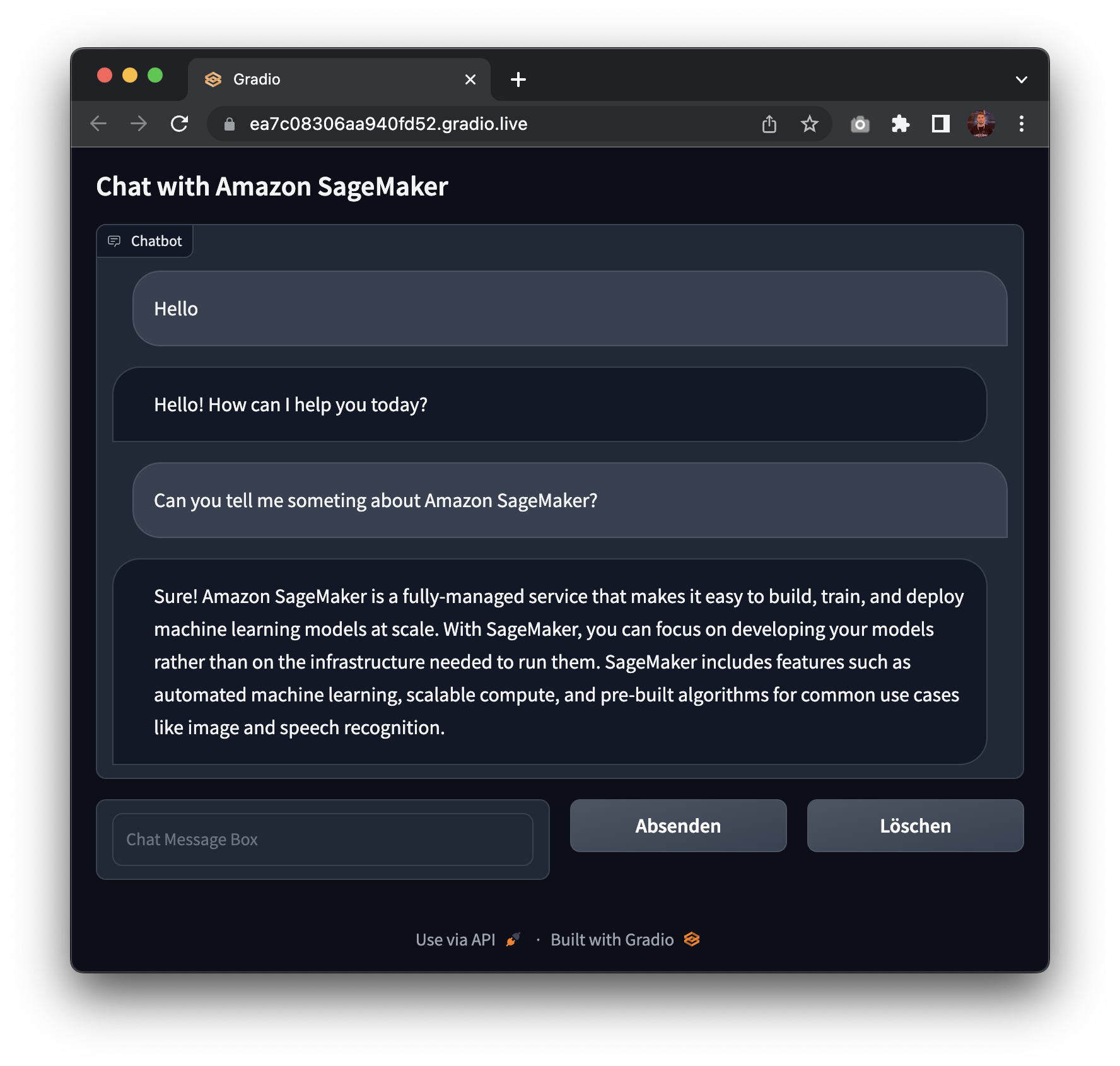
5. Create Gradio Chatbot backed by Amazon SageMaker
We can even create a gradio application to talk with our model. Gradio is a python library that permits you to quickly create customizable UI components around your machine learning models. You could find more about gradio here.
!pip install gradio --upgrade
import gradio as gr
parameters = endoftext
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
gr.Markdown("## Chat with Amazon SageMaker")
with gr.Column():
chatbot = gr.Chatbot()
with gr.Row():
with gr.Column():
message = gr.Textbox(label="Chat Message Box", placeholder="Chat Message Box", show_label=False)
with gr.Column():
with gr.Row():
submit = gr.Button("Submit")
clear = gr.Button("Clear")
def respond(message, chat_history):
converted_chat_history = ""
if len(chat_history) > 0:
for c in chat_history:
converted_chat_history += f"<|prompter|>{c[0]}<|endoftext|><|assistant|>{c[1]}<|endoftext|>"
prompt = f"{converted_chat_history}<|prompter|>{message}<|endoftext|><|assistant|>"
llm_response = llm.predict({"inputs": prompt, "parameters": parameters})
parsed_response = llm_response[0]["generated_text"][len(prompt):]
chat_history.append((message, parsed_response))
return "", chat_history
submit.click(respond, [message, chatbot], [message, chatbot], queue=False)
clear.click(lambda: None, None, chatbot, queue=False)
demo.launch(share=True)
Awesome! 🚀 We’ve successfully deployed Open Assistant Model to Amazon SageMaker and run inference on it. Moreover, we’ve got built a fast gradio application to talk with our model.
Now, it is time so that you can try it out yourself and construct Generation AI applications with the brand new Hugging Face LLM DLC on Amazon SageMaker.
To wash up, we are able to delete the model and endpoint.
llm.delete_model()
llm.delete_endpoint()
Conclusion
The brand new Hugging Face LLM Inference DLC enables customers to simply and securely deploy open-source LLMs on Amazon SageMaker. The straightforward-to-use API and deployment process allows customers to construct scalable AI chatbots and virtual assistants with state-of-the-art models like Open Assistant. Overall, this latest DLC goes to empower developers and businesses to leverage the newest advances in natural language generation.
Thanks for reading! If you will have any questions, be at liberty to contact me on Twitter or LinkedIn.