We’re excited to introduce the Messages API to supply OpenAI compatibility with Text Generation Inference (TGI) and Inference Endpoints.
Starting with version 1.4.0, TGI offers an API compatible with the OpenAI Chat Completion API. The brand new Messages API allows customers and users to transition seamlessly from OpenAI models to open LLMs. The API might be directly used with OpenAI’s client libraries or third-party tools, like LangChain or LlamaIndex.
“The brand new Messages API with OpenAI compatibility makes it easy for Ryght’s real-time GenAI orchestration platform to change LLM use cases from OpenAI to open models. Our migration from GPT4 to Mixtral/Llama2 on Inference Endpoints is effortless, and now we’ve a simplified workflow with more control over our AI solutions.” – Johnny Crupi, CTO at Ryght
The brand new Messages API can also be now available in Inference Endpoints, on each dedicated and serverless flavors. To get you began quickly, we’ve included detailed examples of find out how to:
Limitations: The Messages API doesn’t currently support function calling and can only work for LLMs with a chat_template defined of their tokenizer configuration, like within the case of Mixtral 8x7B Instruct.
Create an Inference Endpoint
Inference Endpoints offers a secure, production solution to simply deploy any machine learning model from the Hub on dedicated infrastructure managed by Hugging Face.
In this instance, we’ll deploy Nous-Hermes-2-Mixtral-8x7B-DPO, a fine-tuned Mixtral model, to Inference Endpoints using Text Generation Inference.
We will deploy the model in only a couple of clicks from the UI, or make the most of the huggingface_hub Python library to programmatically create and manage Inference Endpoints. We exhibit the usage of the Hub library here.
In our API call shown below, we’d like to specify the endpoint name and model repository, together with the duty of text-generation. In this instance we use a protected type so access to the deployed endpoint would require a legitimate Hugging Face token. We also have to configure the hardware requirements like vendor, region, accelerator, instance type, and size. You may try the list of obtainable resource options using this API call, and consider really helpful configurations for select models in our catalog here.
Note: It’s possible you’ll have to request a quota upgrade by sending an email to api-enterprise@huggingface.co
from huggingface_hub import create_inference_endpoint
endpoint = create_inference_endpoint(
"nous-hermes-2-mixtral-8x7b-demo",
repository="NousResearch/Nous-Hermes-2-Mixtral-8x7B-DPO",
framework="pytorch",
task="text-generation",
accelerator="gpu",
vendor="aws",
region="us-east-1",
type="protected",
instance_type="nvidia-a100",
instance_size="x2",
custom_image={
"health_route": "/health",
"env": {
"MAX_INPUT_LENGTH": "4096",
"MAX_BATCH_PREFILL_TOKENS": "4096",
"MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS": "32000",
"MAX_BATCH_TOTAL_TOKENS": "1024000",
"MODEL_ID": "/repository",
},
"url": "ghcr.io/huggingface/text-generation-inference:sha-1734540",
},
)
endpoint.wait()
print(endpoint.status)
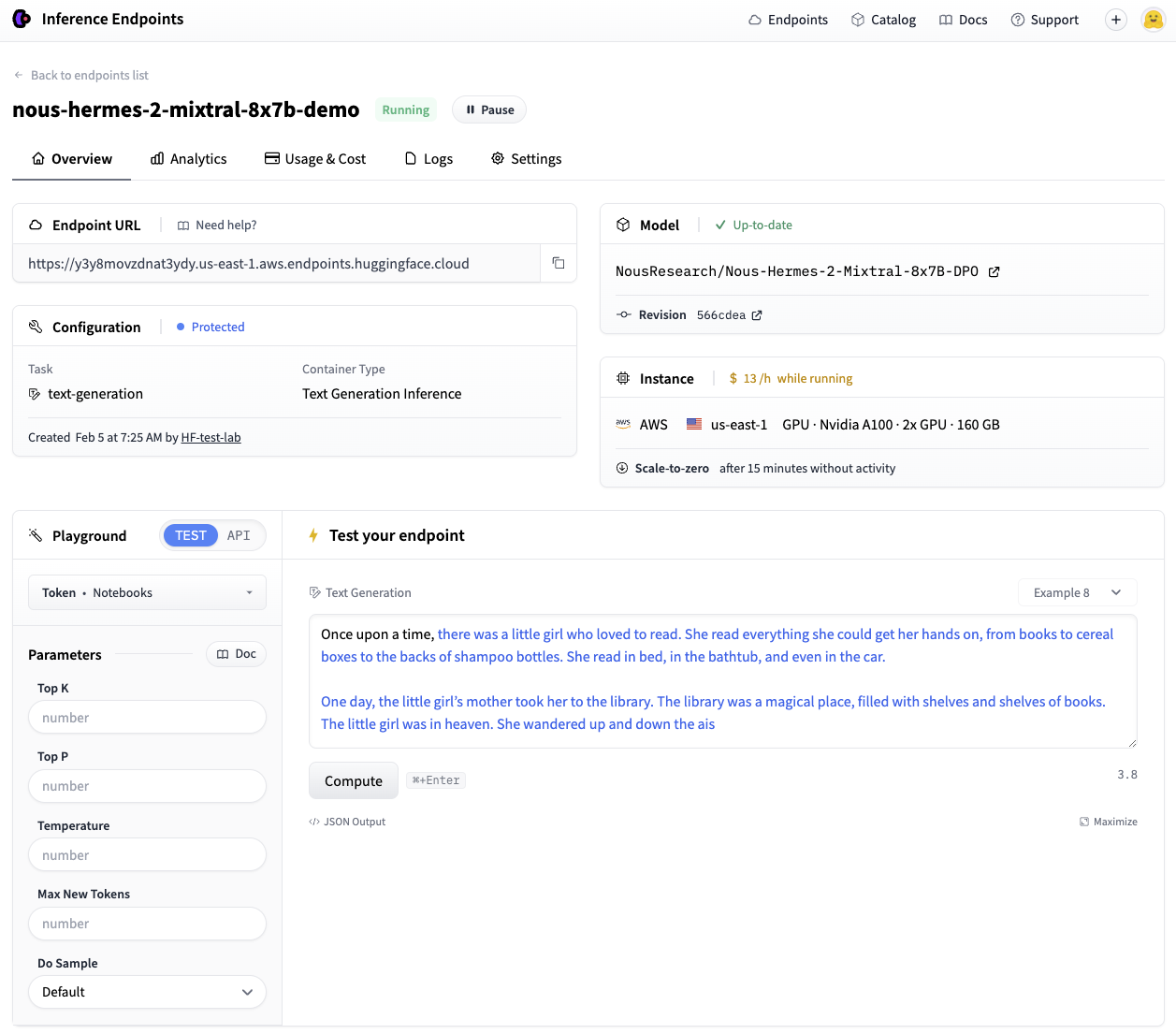
It can take a couple of minutes for our deployment to spin up. We will use the .wait() utility to dam the running thread until the endpoint reaches a final “running” state. Once running, we will confirm its status and take it for a spin via the UI Playground:
Great, we now have a working endpoint!
💡 When deploying withhuggingface_hub, your endpoint will scale-to-zero after quarter-hour of idle time by default to optimize cost in periods of inactivity. Take a look at the Hub Python Library documentation to see all of the functionality available for managing your endpoint lifecycle.
Using Inference Endpoints with OpenAI client libraries
Messages support in TGI makes Inference Endpoints directly compatible with the OpenAI Chat Completion API. Which means any existing scripts that use OpenAI models via the OpenAI client libraries might be directly swapped out to make use of any open LLM running on a TGI endpoint!
With this seamless transition, you may immediately make the most of the various advantages offered by open models:
- Complete control and transparency over models and data
- No more worrying about rate limits
- The power to completely customize systems based on your specific needs
Lets see how.
With the Python client
The instance below shows find out how to make this transition using the OpenAI Python Library. Simply replace the v1/ suffix) and populate the endpoint.url.
We will then use the client as usual, passing an inventory of messages to stream responses from our Inference Endpoint.
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI(
base_url="" + "/v1/",
api_key="" ,
)
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="tgi",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Why is open-source software important?"},
],
stream=True,
max_tokens=500
)
for message in chat_completion:
print(message.selections[0].delta.content, end="")
Behind the scenes, TGI’s Messages API mechanically converts the list of messages into the model’s required instruction format using its chat template.
💡 Certain OpenAI features, like function calling, aren’t compatible with TGI. Currently, the Messages API supports the next chat completion parameters:stream,max_tokens,frequency_penalty,logprobs,seed,temperature, andtop_p.
With the JavaScript client
Here’s the identical streaming example above, but using the OpenAI Javascript/Typescript Library.
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = recent OpenAI({
baseURL: "" + "/v1/",
apiKey: "" ,
});
async function essential() {
const stream = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "tgi",
messages: [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ role: "user", content: "Why is open-source software important?" },
],
stream: true,
max_tokens: 500,
});
for await (const chunk of stream) "");
}
essential();
Integrate with LangChain and LlamaIndex
Now, let’s see find out how to use this newly created endpoint together with your preferred RAG framework.
Easy methods to use with LangChain
To make use of it in LangChain, simply create an instance of ChatOpenAI and pass your
from langchain_community.chat_models.openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(
model_name="tgi",
openai_api_key="" ,
openai_api_base="" + "/v1/",
)
llm.invoke("Why is open-source software vital?")
We’re in a position to directly leverage the identical ChatOpenAI class that we might have used with the OpenAI models. This permits all previous code to work with our endpoint by changing only one line of code.
Let’s now use the LLM declared this manner in an easy RAG pipeline to reply an issue over the contents of a HF blog post.
from langchain_core.runnables import RunnableParallel
from langchain_community.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
loader = WebBaseLoader(
web_paths=("https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents",),
)
docs = loader.load()
hf_embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings(model_name="BAAI/bge-large-en-v1.5")
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=512, chunk_overlap=200)
splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs)
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(documents=splits, embedding=hf_embeddings)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()
prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt")
def format_docs(docs):
return "nn".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
rag_chain_from_docs = (
RunnablePassthrough.assign(context=(lambda x: format_docs(x["context"])))
| prompt
| llm
| StrOutputParser()
)
rag_chain_with_source = RunnableParallel(
{"context": retriever, "query": RunnablePassthrough()}
).assign(answer=rag_chain_from_docs)
rag_chain_with_source.invoke("In line with this text which open-source model is the perfect for an agent behaviour?")
{
"context": [...],
"query": "In line with this text which open-source model is the perfect for an agent behaviour?",
"answer": " In line with the article, Mixtral-8x7B is the perfect open-source model for agent behavior, because it performs well and even beats GPT-3.5. The authors recommend fine-tuning Mixtral for agents to potentially surpass the following challenger, GPT-4.",
}
Easy methods to use with LlamaIndex
Similarly, you too can use a TGI endpoint in LlamaIndex. We’ll use the OpenAILike class, and instantiate it by configuring some additional arguments (i.e. is_local, is_function_calling_model, is_chat_model, context_window). Note that the context window argument should match the worth previously set for MAX_TOTAL_TOKENS of your endpoint.
from llama_index.llms import OpenAILike
llm = OpenAILike(
model="tgi",
api_key="" ,
api_base="" + "/v1/",
is_chat_model=True,
is_local=False,
is_function_calling_model=False,
context_window=32000,
)
llm.complete("Why is open-source software vital?")
We will now use it in the same RAG pipeline. Take into accout that the previous selection of MAX_INPUT_LENGTH in your Inference Endpoint will directly influence the variety of retrieved chunk (similarity_top_k) the model can process.
from llama_index import (
ServiceContext,
VectorStoreIndex,
)
from llama_index import download_loader
from llama_index.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbedding
from llama_index.query_engine import CitationQueryEngine
SimpleWebPageReader = download_loader("SimpleWebPageReader")
documents = SimpleWebPageReader(html_to_text=True).load_data(
["https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents"]
)
embed_model = HuggingFaceEmbedding(model_name="BAAI/bge-large-en-v1.5")
service_context = ServiceContext.from_defaults(embed_model=embed_model, llm=llm)
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(
documents, service_context=service_context, show_progress=True
)
query_engine = CitationQueryEngine.from_args(
index,
similarity_top_k=2,
)
response = query_engine.query(
"In line with this text which open-source model is the perfect for an agent behaviour?"
)
In line with the article, Mixtral-8x7B is the perfect performing open-source model for an agent behavior [5]. It even beats GPT-3.5 on this task. Nonetheless, it's price noting that Mixtral's performance could possibly be further improved with proper fine-tuning for function calling and task planning skills [5].
Cleansing up
After you might be done together with your endpoint, you may either pause or delete it. This step might be accomplished via the UI, or programmatically like follows.
endpoint.pause()
endpoint.delete()
Conclusion
The brand new Messages API in Text Generation Inference provides a smooth transition path from OpenAI models to open LLMs. We will’t wait to see what use cases you’ll power with open LLMs running on TGI!
See this notebook for a runnable version of the code outlined within the post.